Merge points below distance (merge_entities_factor)
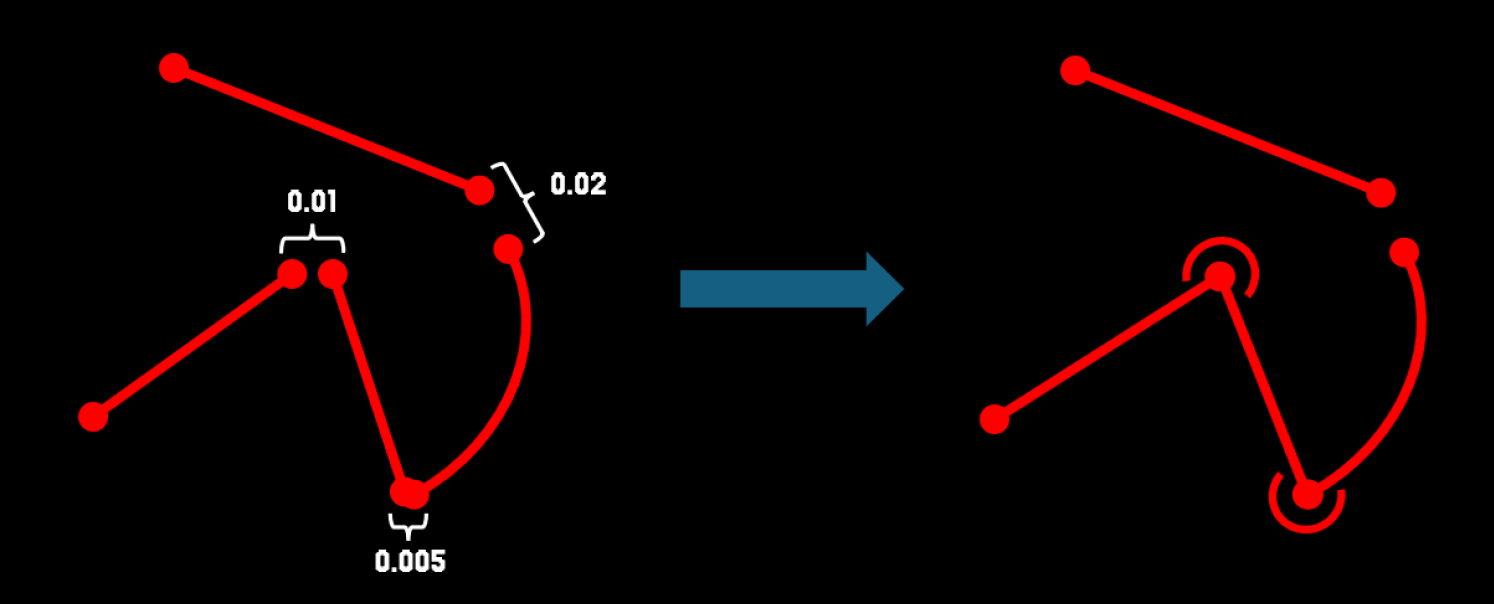
This parameter determines when two lines imported from a DWG/DXF file should be merged.
If the distance between their endpoints is smaller than the parameter value
dist_between_points < merge_entities_factor, the lines are joined and treated as part of the same contour.
In practice, this parameter rarely needs adjustment – the default value works well in almost all cases.
In very specific situations, it may be useful to decrease the value (for example, when two contours are very close to each other and should remain separate), but such cases are uncommon.
Min number of points on arc (arc_min_points)
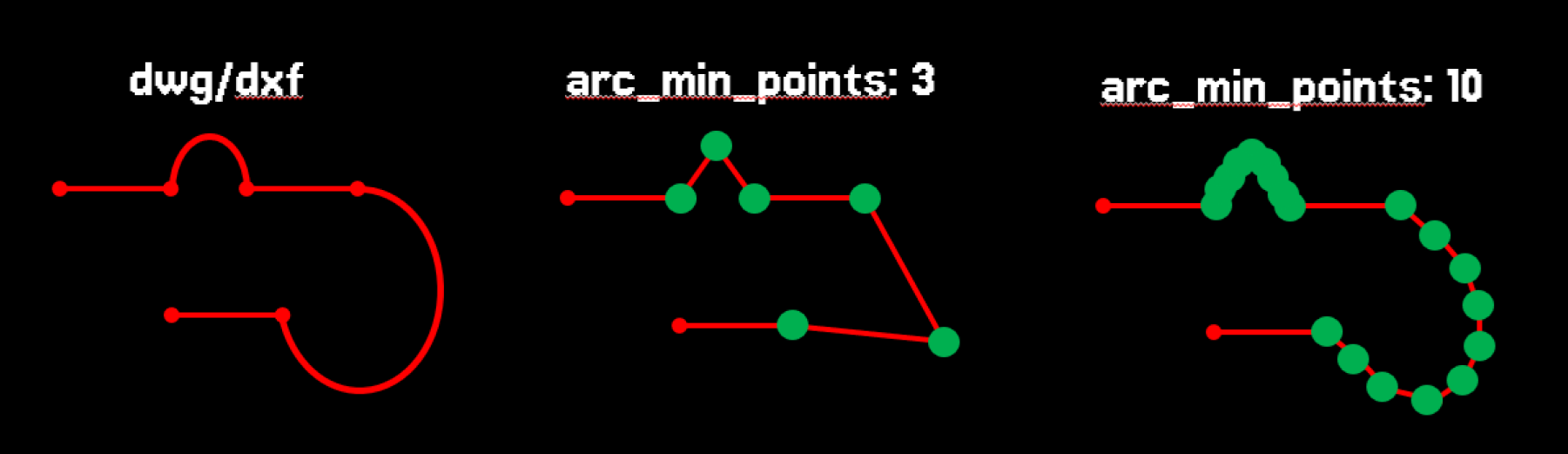
This parameter specifies the minimum number of points used to approximate a curve.
Whether
arc_min_points or arc_approx_len is applied depends on which one results in more points on the curve.
For example, with arc_min_points = 3, every curve will be approximated using at least 3 points.
It is recommended not to set this value too high. Usually, it should be at least 2, as this way the curve is approximated as a simple edge with a start and end point.
The most common recommendation is to set it to 3.
A higher value can be used if there are small circles or holes that you want to approximate as closely as possible to a true circle.
Adjusting this parameter is only necessary if modifying the arc_approx_len parameter does not yield the desired results.
Note that in the preview of the import result, points lying on the curves are marked in green.
Average distance between points on arc (arc_approx_len)
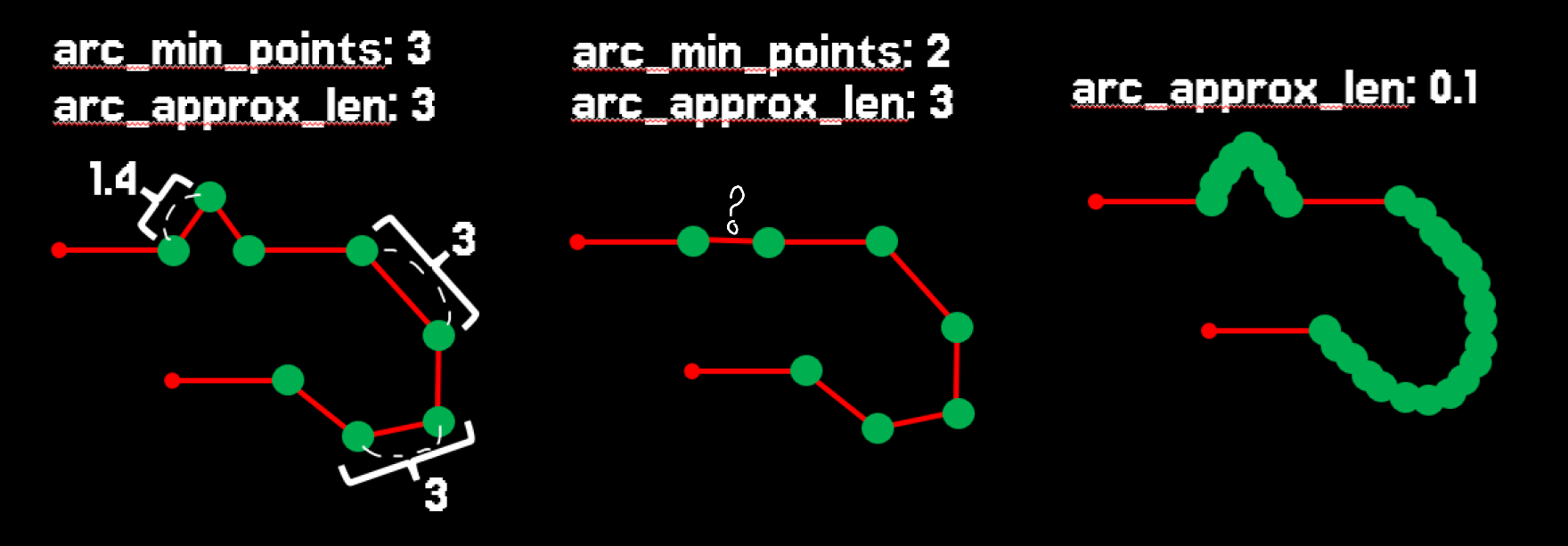
This parameter specifies the average distance between points placed on curves.
The distance is an average value, since the program distributes points as evenly as possible rather than using the exact number.
Whether
arc_min_points or arc_approx_len is applied depends on which one results in more points on the curve.
This parameter is especially useful for approximating large curves, where controlling point spacing helps achieve smoother results.
Note that in the preview of the import result, points lying on the curves are marked in green.
Remove arcs shorter than (arc_skip_len)
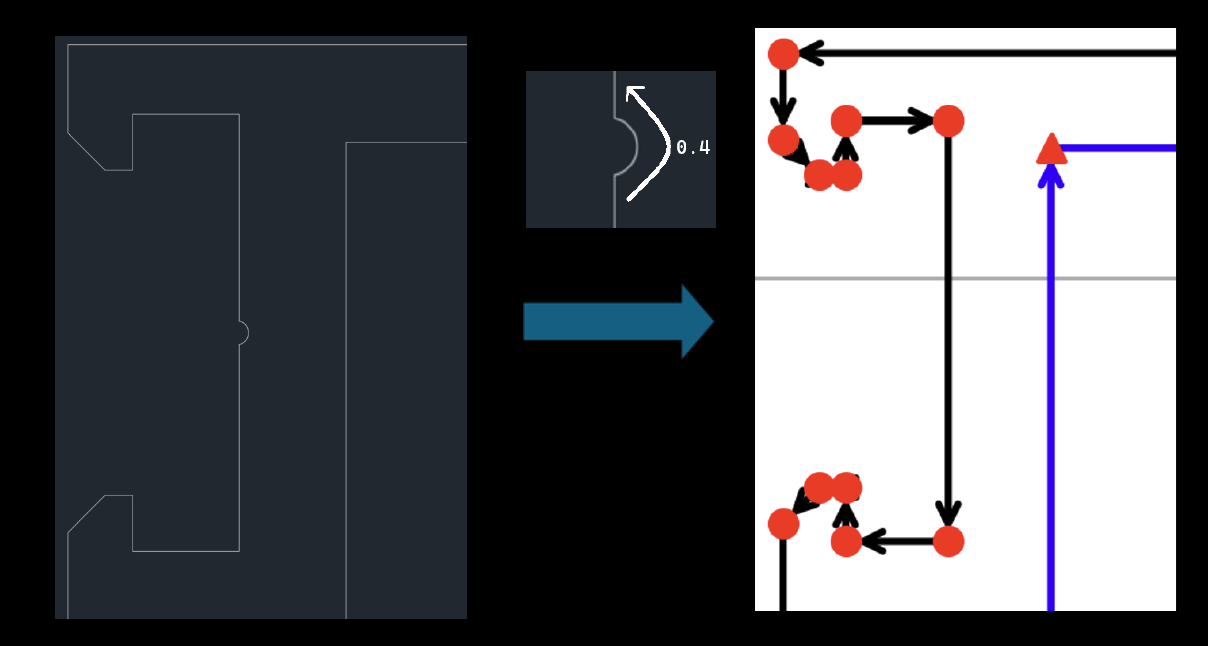
This parameter controls when a curve is discarded. If the arc length is smaller than
arc_skip_len, the curve is skipped (omitted).
It is typically used to remove tiny micro-notches that are represented as curves, preventing the creation of many unnecessary points and improving performance in downstream tools such as Bocad.
This parameter is usually left unchanged, but sometimes there may be micro-cuts or micro-notches in the model that are unnecessary and occur in large numbers. In such cases, it is useful
to set this parameter so that these micro-notches are skipped. Note that this parameter only affects curves, i.e., those marked with green points. Protrusions or notches marked in red are not affected by this parameter.
Remove cuts below surface area (cut_detector_tresh)
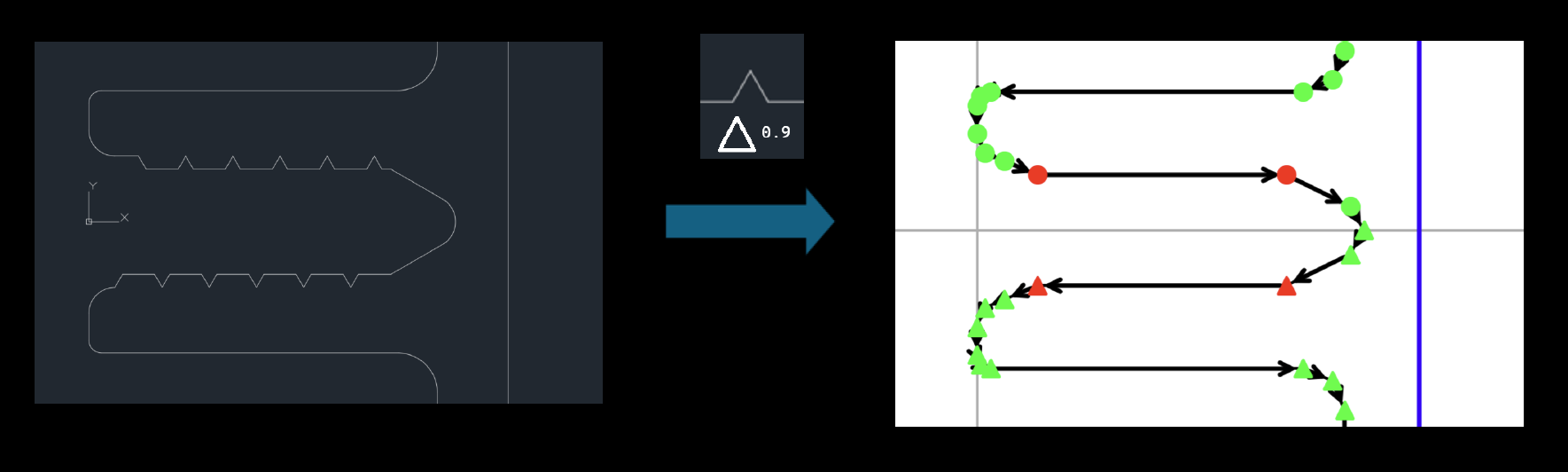
This parameter is used to remove notches. It discards notches that are not curves and are represented by standard red points.
Only notches with an area smaller than the value of this parameter are removed.
This parameter is especially useful when there are many unnecessary notches, which could later reduce model performance due to the creation of excessive points.
Remove spikes below surface area (spike_detector_tresh)
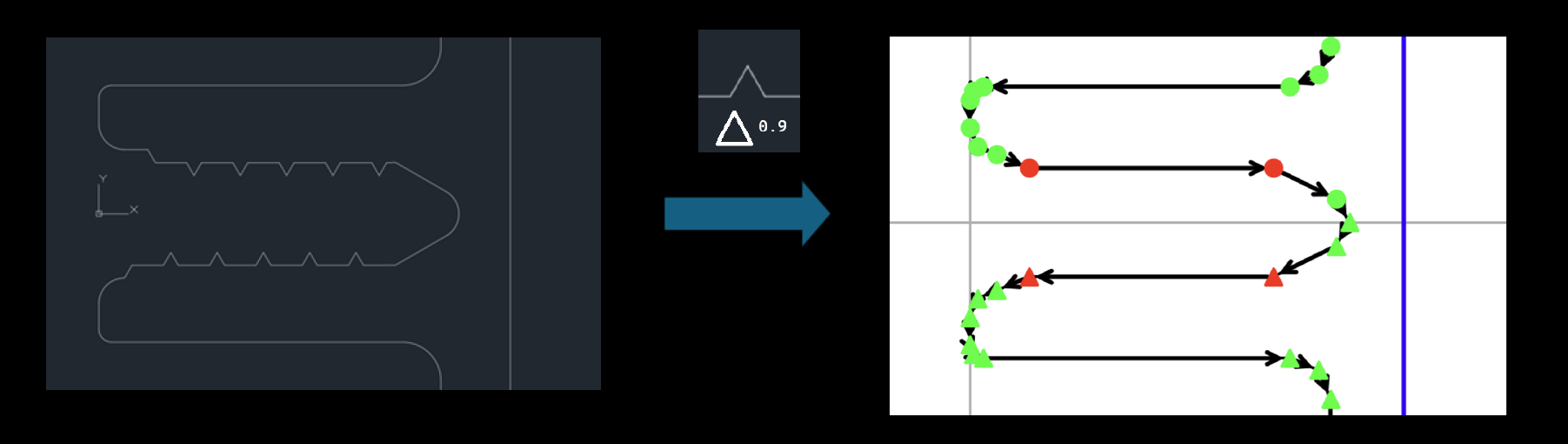
This parameter is used to remove protrusions. It discards protrusions that are not curves and are represented by standard red points.
Only protrusions with an area smaller than the value of this parameter are removed.
This parameter is especially useful when there are many unnecessary protrusions, which could later reduce model performance due to the creation of excessive points.
Apply mirror above similarity score (mirror_activation_tresh)
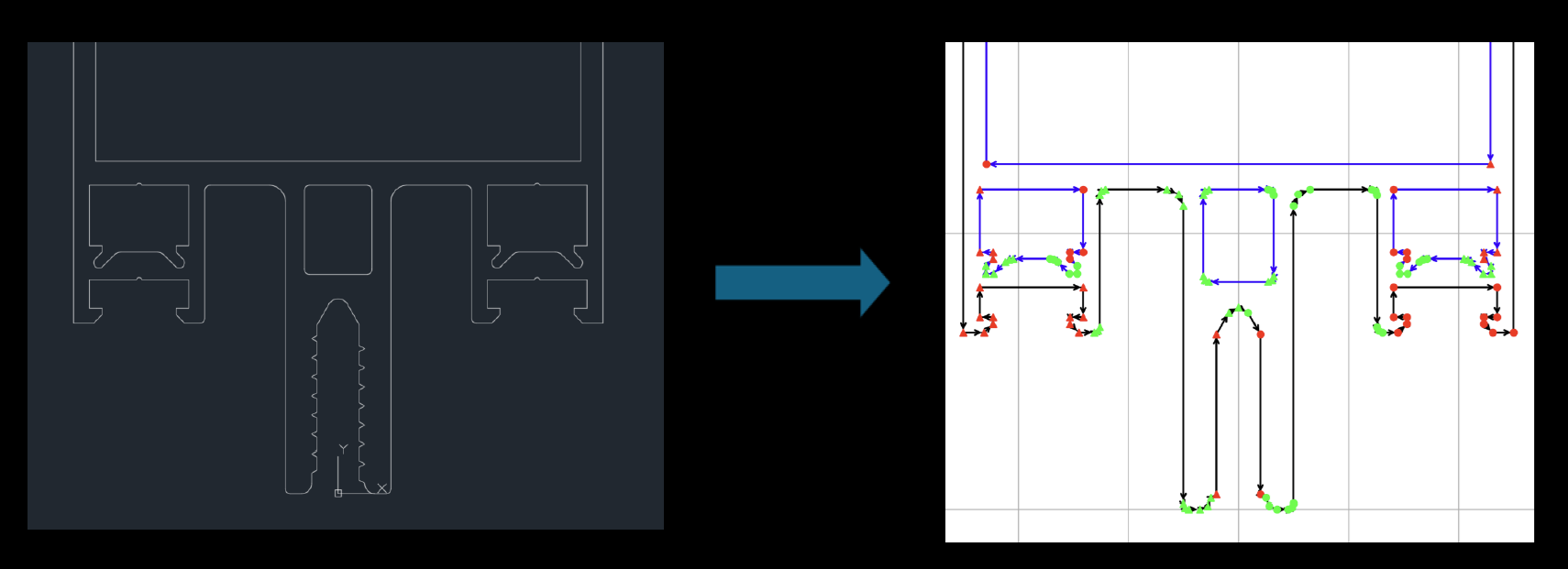
This parameter is used to apply mirror reflection. The mirror is applied only along the vertical and horizontal axes.
The parameter defines the similarity ratio above which the mirror is applied. Points that are mirrored are marked with triangles.
Note that the mirror can be applied simultaneously for both the X and Y axes; this happens almost always in the case of rectangles.
If you do not want the mirror to be applied, set the parameter value to 1 or higher. The recommended value is 0.999.
Min points for automatic arc detection (arc_detector_min_points)
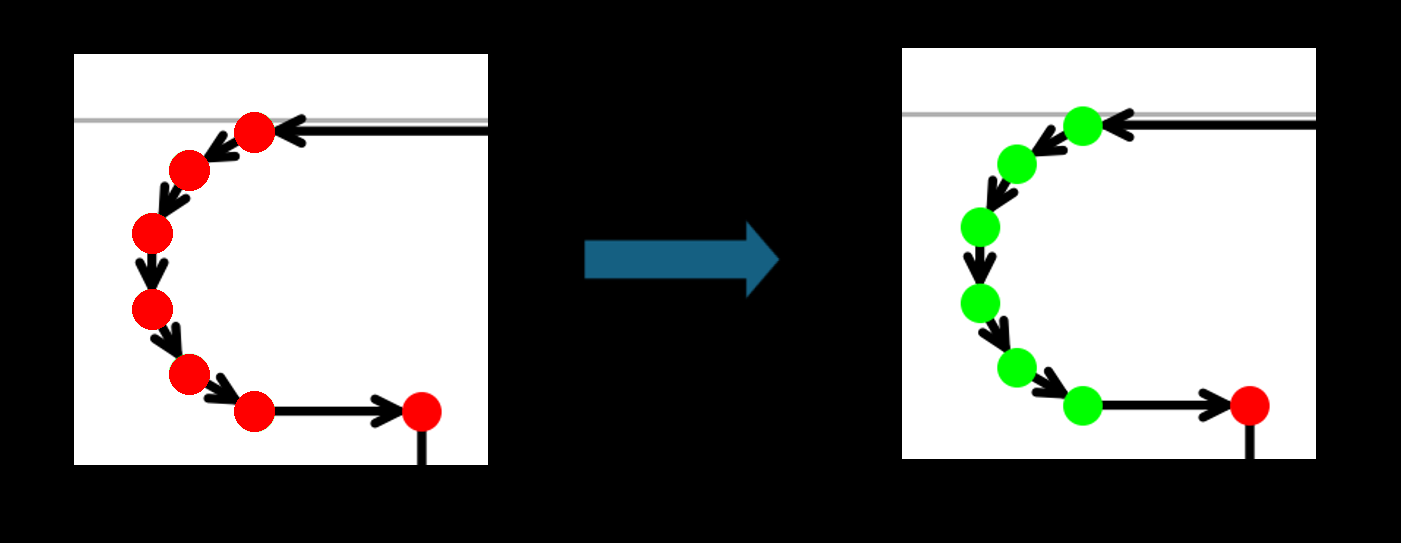
This parameter is responsible for the automatic detection of curves. Sometimes, in the source DWG/DXF file, curves are already approximated by points directly in the file instead of being defined as mathematical curves.
In such cases, these curves are mistakenly not recognized as curves and are marked with red points.
If the program detects curves with a number of points equal to or greater than the value of
arc_detector_min_points, these points are marked as a curve and highlighted in green.
Note: It is generally not recommended to set this value below 4.